Hearing Loss
Causes of Hearing Loss
- Congenital hearing loss (born with a hearing loss)
- Noise exposure
- Natural effects of aging (presbycusis)
- Ototoxic medications (medications that damage the inner ear)
- Genetics
- Stroke or vascular insult to the inner ear
- Disease, such as Meniere’s disease, bacterial meningitis, or otosclerosis
Types of Hearing Loss

Prevalence of Hearing Loss
Age Related Hearing Loss (Presbycusis)
- 30% to 35% of adults aged 65 to 75.
- 40% to 50% of adults aged 75 years and older.
Congenital Hearing Loss
- 5 to 6 infants per 1000 born with some degree of hearing loss
- 2 to 3 infants per 1000 born with moderate to profound hearing loss bilaterally (in both ears)
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
- 12.5% of children aged 6 – 19 years (5.2 million)
- 17% of adults aged 20 – 69 years (26 million)
Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection)
- The most common medical diagnosis in preschool-aged children.
- Approximately 90% of children have at least one episode by age 2 years.
- Approximately 30% of children have at least 6 episodes by age 7 years
Effects of Hearing Loss
Adults
- Speech and other sounds seem muffled
- Difficulty understanding words, especially in background noise or a crowd
- Frequently misunderstands what is said and asks for things to be repeated
- Needing to turn up the volume of the television or radio
- Difficulty identifying and localizing sounds
- Withdrawal from conversations
- Avoidance of some social settings

Children
- Speech-language delays, unclear speech, limited or no spoken language
- Difficult to consistently get your child’s attention Your child frequently says “huh” or “what”
- Your child responds inconsistently to sound
- History of ear infections and/or ear aches
- Your child seems to watch the speaker’s face carefully when talking
- Your child’s own voice seems to soft or too loud
- Your child turns the radio or television louder than normal
- Your child confuses sounds that are similar
- Your child often answers a question with an unrelated answer
- Your child seems inattentive at home or at school
- Unexplained behavioral problems
Benefits of Treating Hearing Loss
Adults
- Improve the ability to effectively communicate
- Help prevent the social isolation that can occur when someone has a hearing loss
- Improve awareness of environmental sounds


Children
- Improve speech and language development
- Improve learning in school
- Improve social interactions and the ability to make friends
- Improve the ability to effectively communicate
- Improve awareness of environmental sounds
Noise Induced Hearing Loss
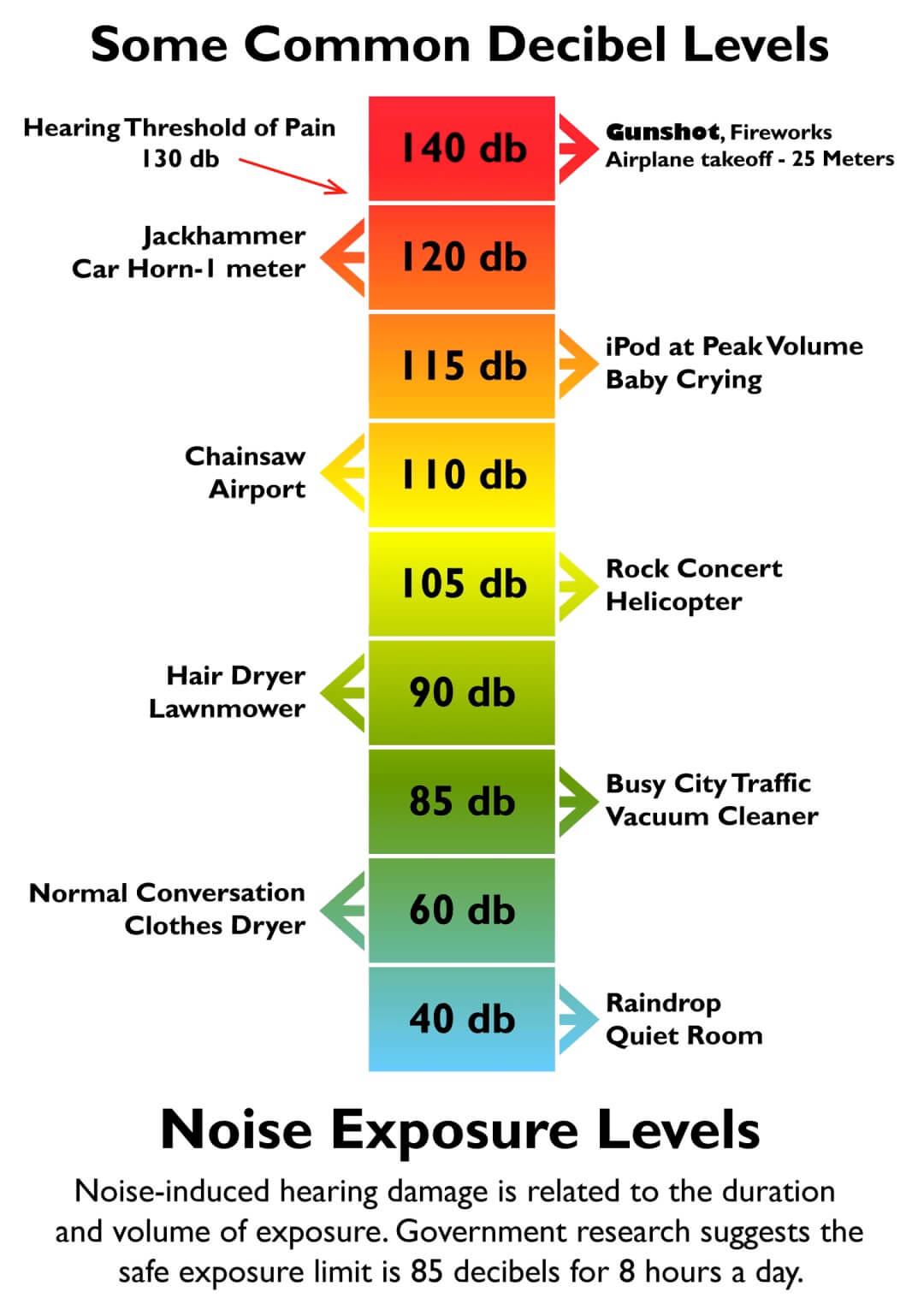
Levels that can cause permanent hearing loss:
- Exposure to sounds over 120 dB
- Extended or repeated exposure to sounds over 85 dB
Typical Sound Levels:
|
firearms |
140 dB |
|
jackhammer |
130 dB |
|
siren |
120 dB |
|
lawn mower |
106 dB |
|
hand drill |
100 dB |
|
passing motorcycle |
90 dB |
|
hair dryer, food processor |
80 - 90 dB |
|
vacuum cleaner |
70 dB |
|
typical conversation |
60 dB |
|
moderate rainfall |
50 dB |